Peroneal nerve palsy. The neurologist found a palpable lesion on the dorso lateral aspect of the knee.
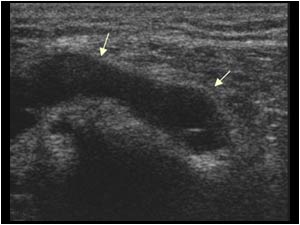
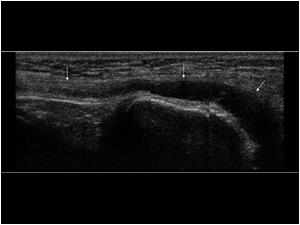
It is well known that ganglia arising from the tibiof ibular joint space can cause peroneal nerve compression. In this case there seemed to be not only compression of the nerve but an actual relation of the lesion to the nerve. The patient was operated in a university hospital. The lesion proved to be a ganglion cyst of the peroneal nerve sheath. After removal of the lesion the peroneal nerve palsy resolved quickly.
For more peripheral nerve lesions see cases 7.3.3, for more tibiofibular ganglia see cases 6.6.8: